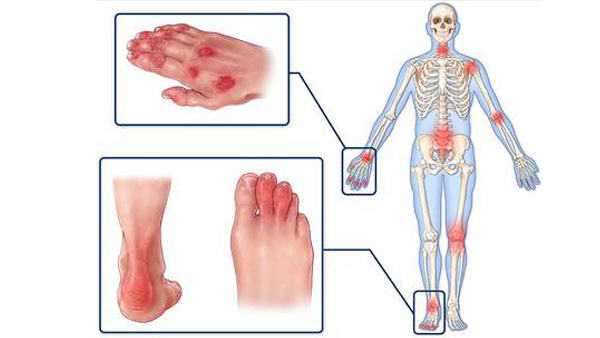
RHEUMATOLOGY
Rheumatology is a super specialized branch of internal medicine devoted to diagnosis and therapy of rheumatic diseases. Clinicians who specialize in rheumatology are called rheumatologists. Rheumatologists deal mainly with clinical problems involving joints, soft tissues, autoimmune diseases, vasculitis, and heritable connective tissue disorders.
Rheumatology is a rapidly evolving medical specialty, with advancements owing largely to new scientific discoveries related to immunology of these disorders. Because characteristics of some rheumatological disorders are often best explained by immunology, pathogenesis of many major rheumatological disorders are now described in terms of the autoimmune system, i.e. as an autoimmune disease.
Correspondingly, most new treatment modalities are also based on clinical research in immunology and the resulting improved understanding of the genetic basis of rheumatological disorders. Future treatment may include gene therapy as well. At present evidence-based medical treatment of rheumatological disorders has helped patients with rheumatism lead a near-normal life.
Scleroderma
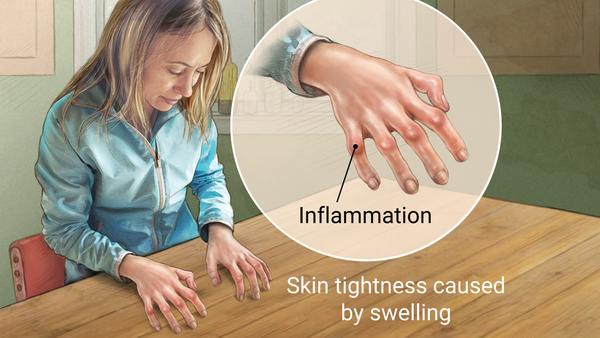
Scleroderma is a connective tissue disease that involves tightening of skin. It can involve blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs as lungs and kidneys. It is a type of autoimmune disorder, a condition that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissue.
Gout
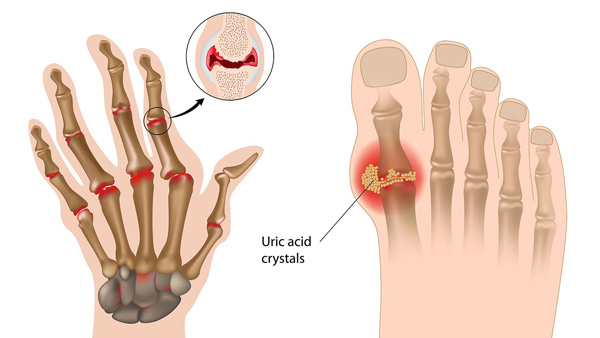
Gout is a kind of arthritis that occurs when uric acid builds up in blood and causes joint inflammation. There are two types of gouts; acute gout and chronic gout. Acute gout is a painful condition that typically affects one joint and chronic gout is repeated episodes of pain and inflammation, which may involve more than one joint.
Ankylosing spondylitis
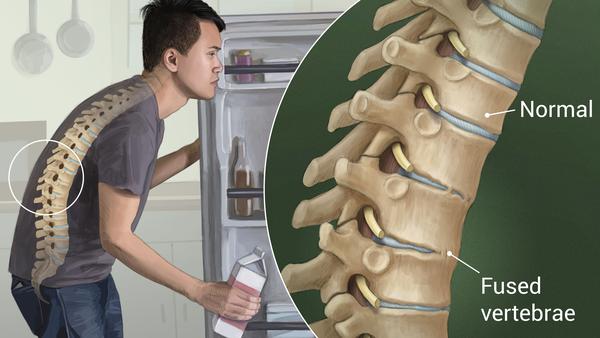
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the axial skeleton with variable involvement of peripheral joints and nonarticular structures. Ankylosing spondylitis is a form of spondyloarthritis, a chronic, inflammatory arthritis and autoimmune disease. It mainly affects joints in the spine and the sacroiliac joint in the pelvis, and can cause eventual fusion of the spine.
Peadiatric Rheumatology
Pediatric rheumatology is a specialty were rheumatologists are specifically trained to be highly skilled in managing various arthritis conditions and autoimmune diseases as Juvenile idiopathic arthritis(earlier called as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis), SLE, myositis, localised scleroderma and various immunodeficiency disease.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
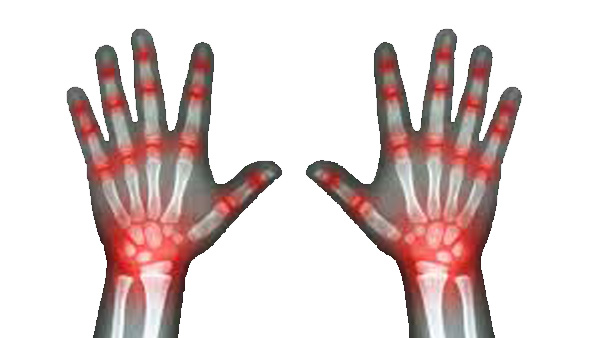
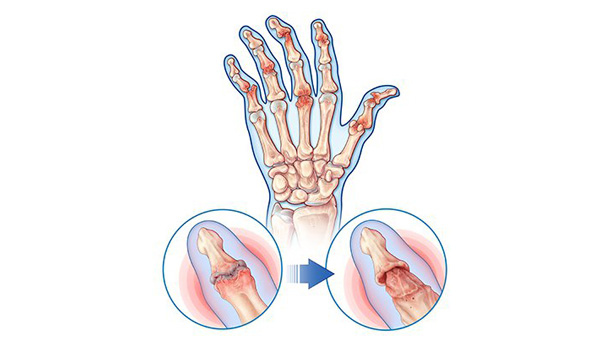
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It can also affect other organs. Causes, incidence, and risk factors are follows:
- The cause of Rheumatoid arthritis is unknown. It is an autoimmune disease, which means the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue.
- Rheumatoid arthritis can occur at any age, but is more common in middle age. Women get Rheumatoid arthritis more often than men.
- Infection, genes, and many other factors may be linked to the disease.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that often occurs with psoriasis of the skin.The Causes, incidence, and risk factors are follows:
- Psoriasis is a common, chronic skin condition that causes scaly patches on the body. About 1 in 30 people with psoriasis will develop arthritis with the skin condition. In most cases, psoriasis comes before the arthritis.
- The cause of psoriatic arthritis is not known, but genes may play a role. In general, people who have psoriasis have a higher rate of arthritis than the general population.
Vasculitic disorders
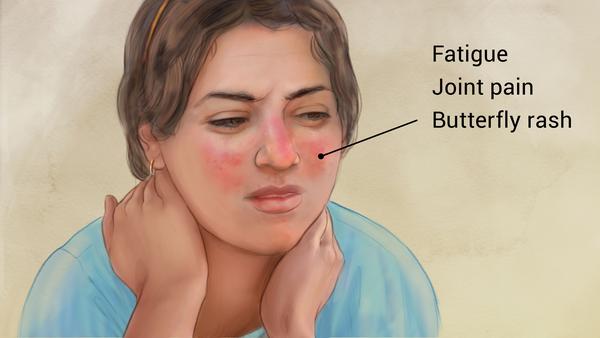
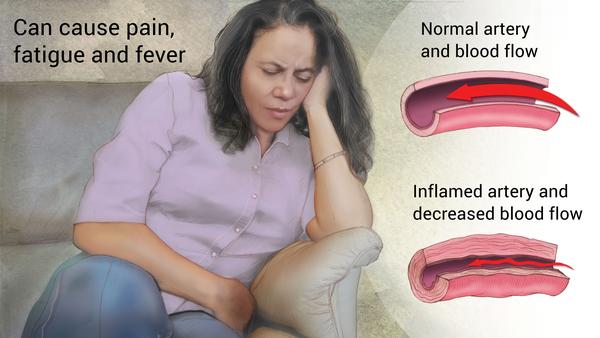
Vasculitis refers to a heterogeneous group of disorders that are characterized by inflammatory destruction of blood vessels wherein both the arteries and veins are affected. Vasculitides can be classified by the type or size of the blood vessels. Different vasculitis syndromes presents with various manifestations. It can causes fever, Joint pain, fatigue, skin rashes, weight loss, nerve involvent, lung and kidney involvement. They need aggressive immunosupression for their treatment.
Reactive Arthritis
Reactive arthritis is a group of inflammatory conditions that involves the joints, urethra, and eyes. There may also be sores (lesions) on the skin and mucus membranes. The Causes, incidence, and risk factors are follows:
- The exact cause of reactive arthritis is unknown. It occurs most commonly in men before the age of 40. It may follow an infection with Chlamydia, Campylobacter, Salmonella, or Yersinia. Certain genes may make you more prone to the syndrome.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a common syndrome in which a person has generalised pain and tenderness in the joints, muscles, tendons, and other soft tissues. Fibromyalgia has also been linked to fatigue, sleep problems, headaches, depression, and anxiety.
Consultation Fees
First Consultation: ₹1900/-
Follow-up Consultation: ₹1400/-
Online Consultation: ₹1800/-
Note: Consultation fees is valid for 7 days only.